In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, Quick Commerce (Q-commerce) has emerged as a dominant force, reshaping how businesses cater to the increasing demand for instant delivery. At the heart of Q-commerce lies the concept of dark stores—retail spaces that serve as fulfillment centers for online orders, often operating in the background with no direct customer interaction. These dark stores are crucial to providing the quick turnaround times that Q-commerce promises. To understand and optimize the performance of these dark stores, businesses, and data analysts are increasingly turning to Web Scraping Q-commerce Dark Store Data techniques to gather valuable insights.
As the Q-commerce industry grows, Web Scraping Quick Commerce data has become an essential tool for businesses aiming to enhance their operational efficiency, monitor market trends, and optimize inventory management. With the right scraping strategies, companies can gain real-time data on product availability, pricing, demand patterns, and competitor performance, helping them stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
What is Q-Commerce?
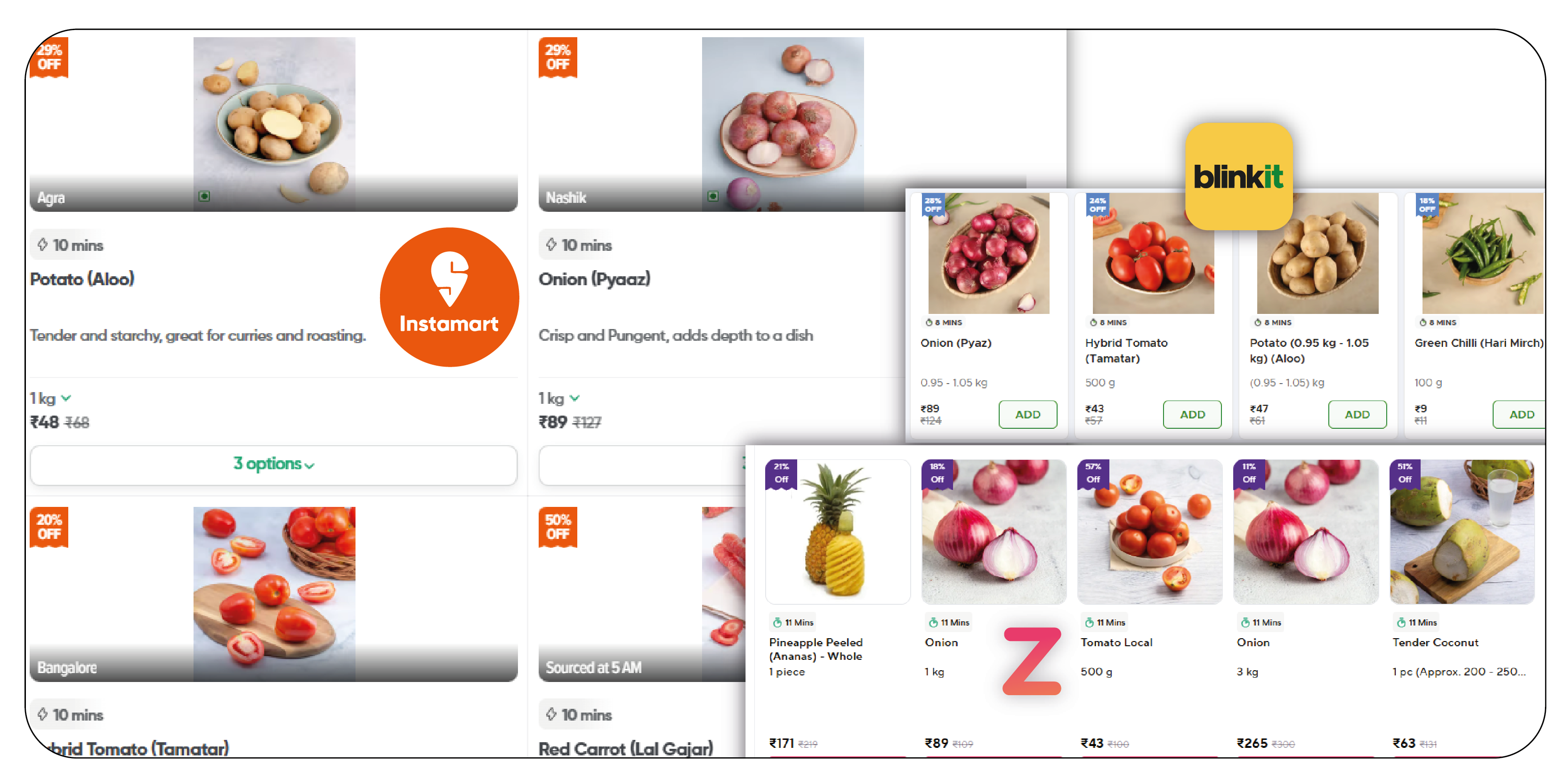
Quick Commerce, also known as Q-commerce, refers to a subset of e-commerce that focuses on providing rapid delivery, typically within an hour. Unlike traditional e-commerce, which may involve longer shipping times, Q-commerce relies on local dark stores and optimized logistics to ensure that products reach customers as quickly as possible. These dark stores are typically situated in urban areas and are not open to the public, but they house inventories that can be quickly picked up and packed for delivery.
Key players in the Q-commerce space include platforms like Blinkit, Zepto, Grofers, and Instamart. These companies thrive on the efficiency of their dark stores and the speed of their deliveries, focusing on groceries, essentials, and other high-demand products. To optimize operations and stay competitive, businesses increasingly turn to Scrape Dark Store Data for Q-commerce and FMCG Websites. By leveraging Dark Store Data Scraping, they can access real-time inventory data, track pricing changes, and gain insights into customer preferences, ensuring timely deliveries and better market positioning.
The Role of Dark Stores in Q-Commerce
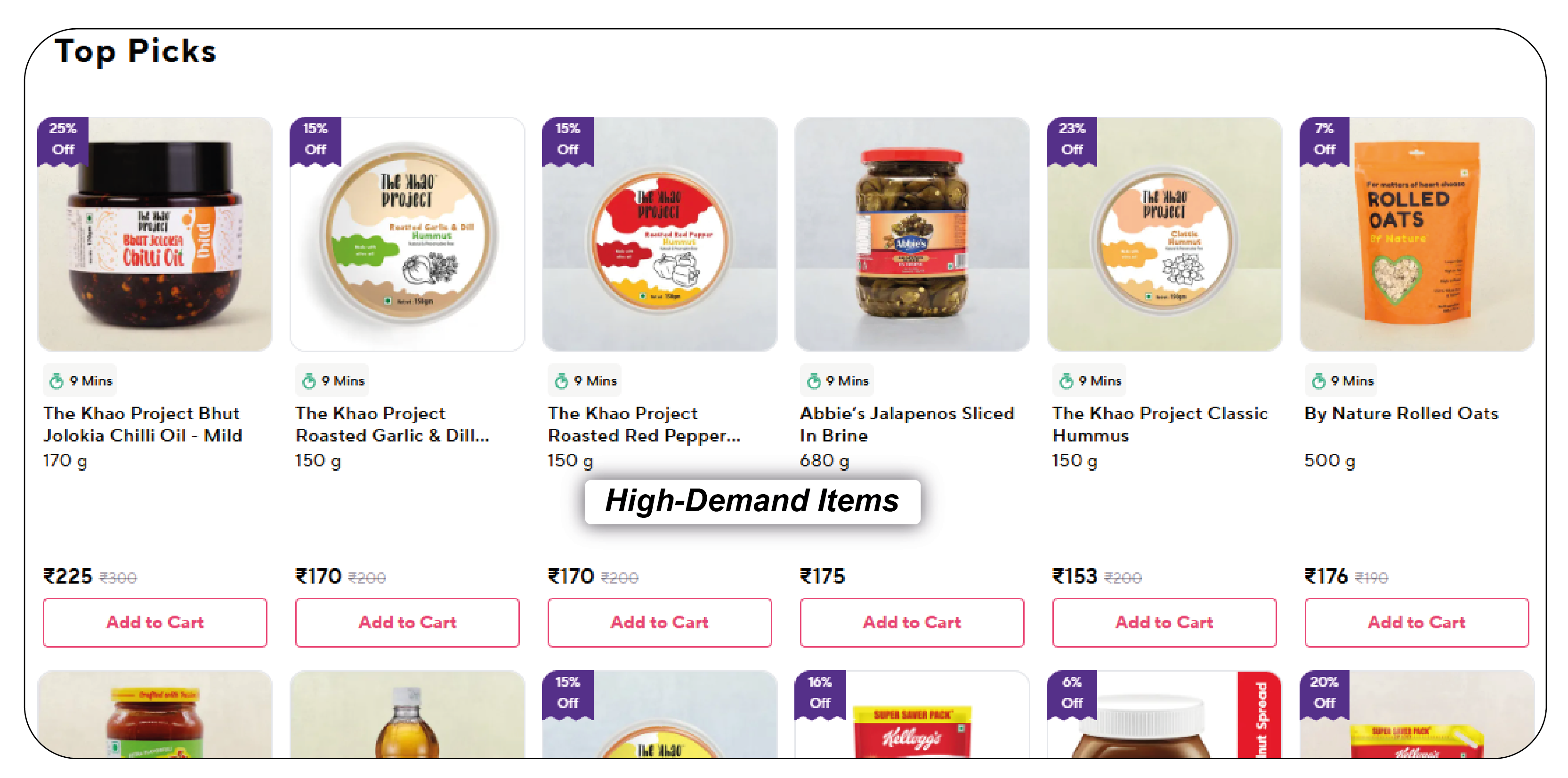
Dark stores play a pivotal role in the Q-commerce model. These are specialized warehouses or retail spaces designed solely to fulfill online orders. This allows businesses to streamline operations, reduce overhead costs, and optimize inventory management. In a dark store, products are organized to facilitate fast picking and packing orders for immediate dispatch. This efficiency enables Q-commerce companies to promise and deliver rapid delivery times—usually within an hour or two.
Dark stores typically store high-demand items such as groceries, snacks, personal care products, and household essentials. However, there are also specialized dark stores focused on particular product categories. As Q-commerce grows, the demand for more tailored and localized dark store data increases, prompting businesses to use web scraping to capture insights from these locations. By implementing FMCG Product data Collection strategies, companies can track fast-moving consumer goods across dark stores and ensure their stock levels meet demand. Additionally, businesses often rely on scraping tools to Extract Grocery and Supermarket Data, enabling them to monitor real-time availability and pricing, optimize inventory, and enhance customer experience.
Why Web Scraping Dark Store Data?
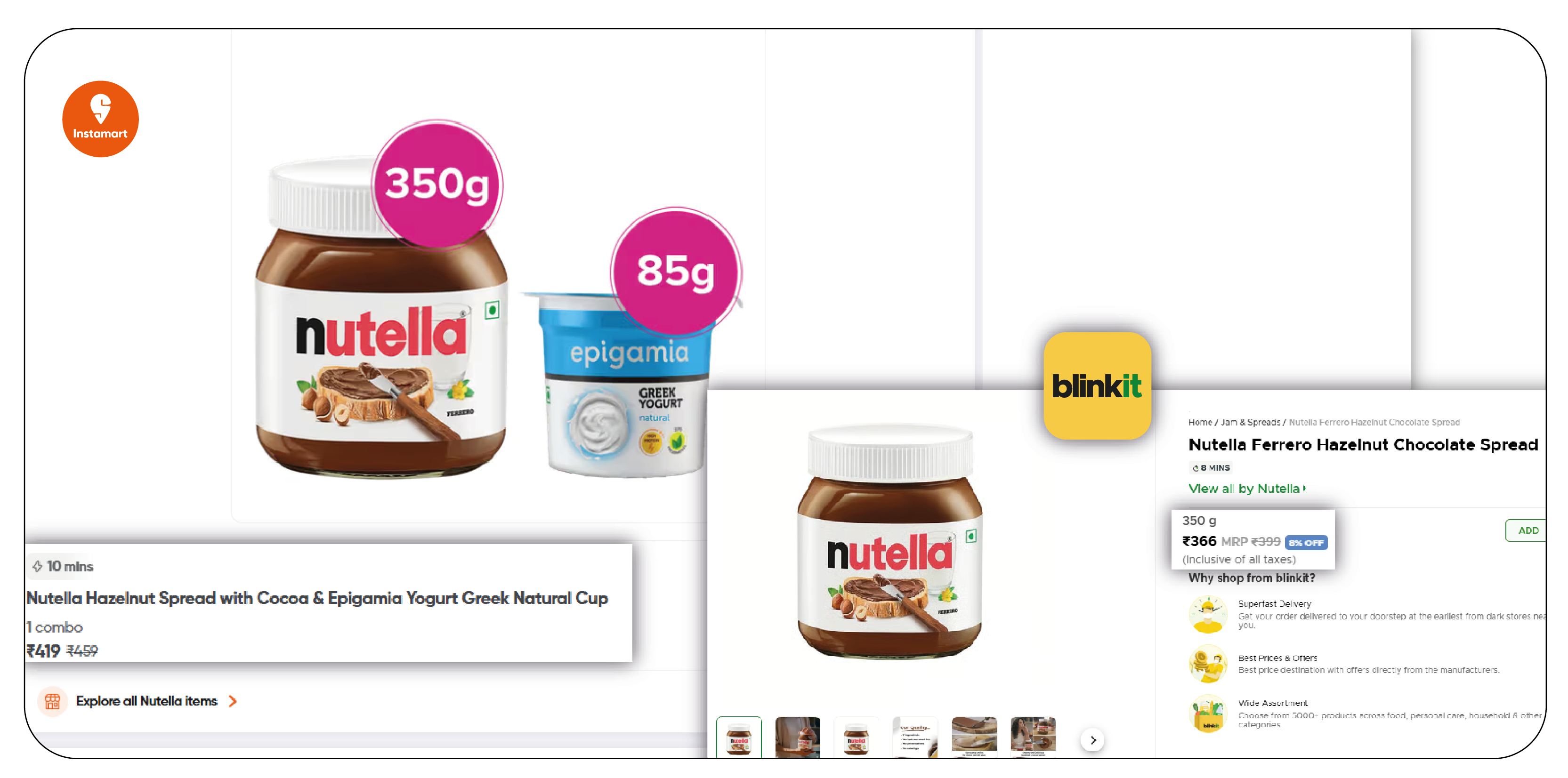
Web scraping extracts data from websites and online platforms to gather valuable business insights. When applied to Q-commerce and dark stores, web scraping can unlock a wealth of information, including inventory data, product pricing, demand patterns, and competitor analysis. This data can then be used to optimize inventory management, pricing strategies, and marketing efforts.
The following are some of the main reasons why businesses need to scrape Q-commerce dark store data:
• Inventory Monitoring and Optimization: Dark stores are designed to handle high volumes of orders with limited inventory. Web Scraping E-commerce Websites enable businesses to monitor product availability in real-time across multiple Q-commerce platforms. By tracking which products are in stock or out of stock, companies can adjust their inventory in response to demand fluctuations. This can help prevent overstocking or understocking of items, thus ensuring a smooth supply chain and avoiding delivery delays.
• Pricing Insights: Pricing is one of the most important aspects of competitive e-commerce. Web Scraping E-commerce Websites and dark store data allow companies to track competitor pricing in real time and make informed decisions about their Pricing Strategies. This is crucial in a space where Q-commerce companies are trying to capture market share by offering competitive prices, discounts, or bundles. By scraping pricing data from various dark stores, businesses can also spot pricing trends, monitor fluctuations, and adjust prices to stay competitive.
• Customer Behavior Analysis: Scraping dark store data provides valuable consumer behavior and preferences insights. By analyzing which products are being searched for or frequently purchased, businesses can better understand customer needs. This insight can help forecast demand for particular items, improve product recommendations, and design personalized marketing strategies. Scraping reviews and ratings can also give businesses feedback about product quality and customer satisfaction, which is critical to improving the customer experience. Businesses can also gather valuable QuickCommerce and FMCG datasets to understand customer preferences better.
• Market Trends and Demand Patterns: Q-commerce thrives on meeting immediate consumer demand, making it essential to stay ahead of market trends. Web Scraping E-commerce Websites help identify emerging trends in product demand, seasonal preferences, and shifts in consumer behavior. By scraping data from multiple Q-commerce platforms, businesses can identify hot-selling items, monitor demand spikes, and adjust their inventory and promotional efforts accordingly.
• Location-Based Insights: Since dark stores are often located in densely populated urban areas to facilitate quick deliveries, businesses can use web scraping to understand geographical trends and optimize delivery routes. For example, scraping data about delivery times, product availability in specific locations, and demand patterns in particular regions helps businesses decide where to set up new dark stores. Scraping this localized data enables businesses to target specific areas with tailored offerings and efficient delivery solutions.
• Competitor Intelligence: In any rapidly evolving market, knowing your competitors' actions is essential to staying ahead. Price Monitoring allows businesses to track competitor product offerings, prices, and inventory levels across multiple Q-commerce platforms. This competitive intelligence can help companies adjust their strategies, identify gaps in the market, and gain a competitive edge by offering better deals, exclusive products, or faster delivery times.
Critical Challenges in Scraping Q-Commerce Dark Store Data
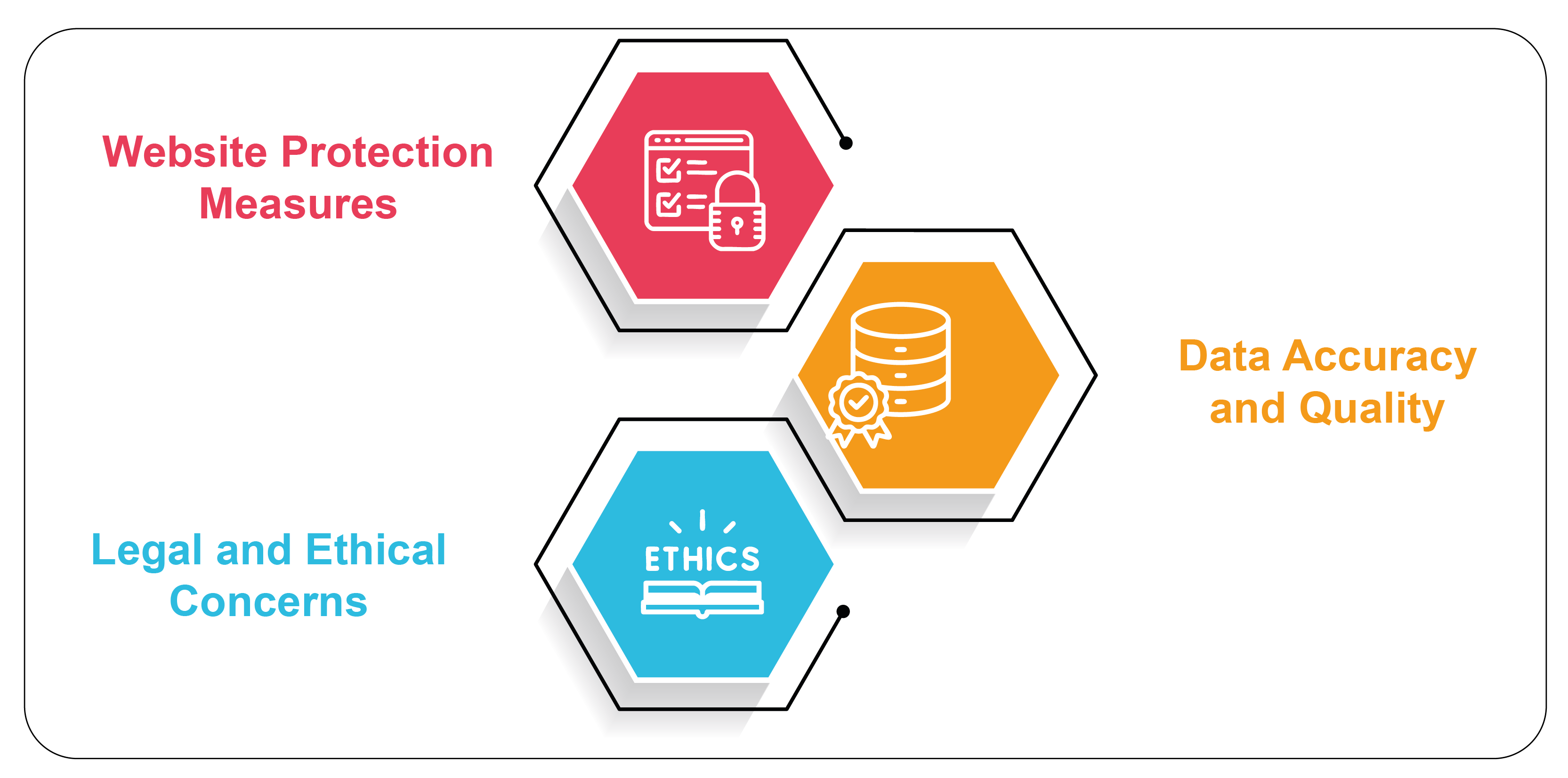
While web scraping offers numerous advantages, it has its challenges. Here are some of the critical obstacles businesses may face when scraping Q-commerce dark store data:
1. Website Protection Measures
Many Q-commerce platforms take measures to protect their data from scraping, such as implementing CAPTCHAs, IP blocking, or rate limiting. Overcoming these protections requires advanced scraping techniques like rotating IPs, proxies, or CAPTCHA-solving services. These measures can increase the complexity and cost of scraping efforts.
2. Data Accuracy and Quality
When scraping large amounts of data, businesses must ensure that the data collected is accurate and up-to-date. Since Q-commerce is fast-moving and inventory levels change quickly, scraping outdated or inaccurate data can lead to poor business decisions. Proper monitoring and quality control mechanisms must be in place to ensure the integrity of the scraped data.
3. Legal and Ethical Concerns
When done without permission, web scraping can raise legal and ethical concerns. Businesses must navigate data privacy laws, terms of service agreements, and copyright laws to avoid legal issues. It's essential to scrape data responsibly and ensure it is used within the law.
Conclusion
Web scraping Q-commerce dark store data has become an invaluable tool for businesses looking to optimize their operations, understand market trends, and gain a competitive edge. As the Q-commerce industry continues to grow, the ability to gather and analyze data from dark stores will become increasingly important. While challenges such as data accuracy and legal considerations exist, the benefits of scraping this data—such as improved inventory management, dynamic pricing, and customer insights—far outweigh the hurdles. Businesses that harness the power of web scraping will be well-positioned to lead in the ever-evolving world of Q-commerce.
At Product Data Scrape, we strongly emphasize ethical practices across all our services, including Competitor Price Monitoring and Mobile App Data Scraping. Our commitment to transparency and integrity is at the heart of everything we do. With a global presence and a focus on personalized solutions, we aim to exceed client expectations and drive success in data analytics. Our dedication to ethical principles ensures that our operations are both responsible and effective.




































.webp)






